Design Online Coding Platform CODING BLOX (Design Leetcode LLD)
- Coding Blox is an Online Coding Platform that allows a user to Sign Up, Create Contests and participate in Contests hosted by Others.
- Each contest can have a level (LOW, MEDIUM, HIGH) and will contain a set of questions.
- Each question will have different levels of difficulty(LOW, MEDIUM, HIGH) and score.
- Based on the contest level, the question set is going to be decided. Contest level with LOW difficulty will have questions with LOW difficulty level.
- Final score will be decided based on the difficulty LEVEL chosen for a contest
- Users solve problems and get points based on the difficulty of the problems and after the contests scores of the users are updated.
Functionalities/Requirements:
- CreateUser <user_name>
- CreateQuestion <difficulty_level>
- ListQuestion <difficulty_level>
- CreateContest <contest_name> <contest_level> <contest_creator_user_name>
- ListContest <difficulty_level>
- AttendContest <contest_id> <user_name>
- RunContest <contest_id> <contest_creator_user_name>
- LeaderBoard <sorting order asc/desc>
- ContestHistory <contest_id>
- WithdrawContest <contest_id>
full problem statement & solution (Time given 90min) : http://bit.ly/leetcode-low-level-design
Simply I follow these steps for any LLD.
- Find out entities
- Find out the relationship between entities
- Write entities CRUD (use hashmap or JPA)
- Start implementing requirements
Step 1,2 and 3 => approx 30min
Step 4 => +1hr
Step 1, 2: Domain layer
Step 3: Database/dao layer
Step 4: Service layer
(Use this hashmap template to quick start: http://bit.ly/lld-hashmap-as-db-template )
Step 0: Understand the problem statement and requirements
Step 1: List down important entities/model/domain
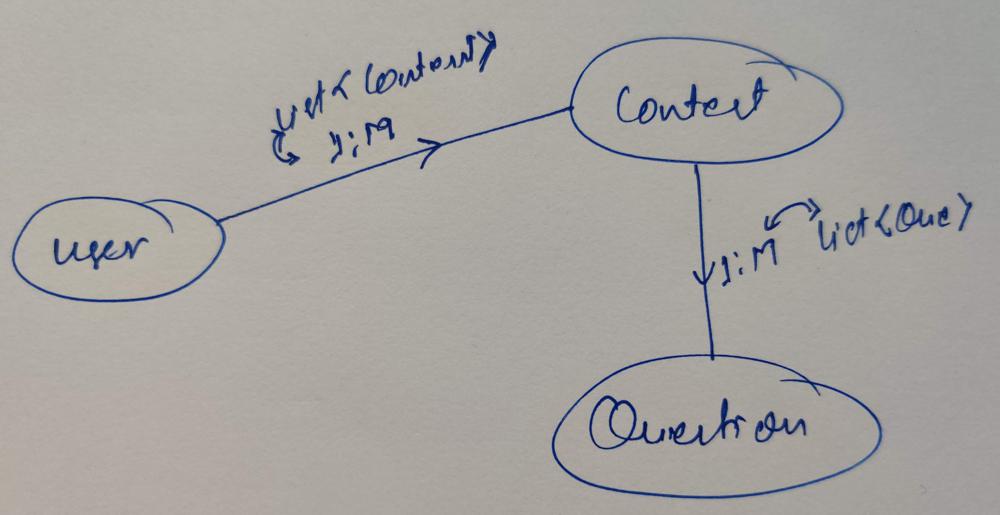
In the above question list of entities are -> User, Contest, and Question

Step 2: List down the relationship between entities.
e.g.
User can register for multiple contests
User:
List<Contest> contests
The contest can have multiple Questions
Contest:
List<Question> questions
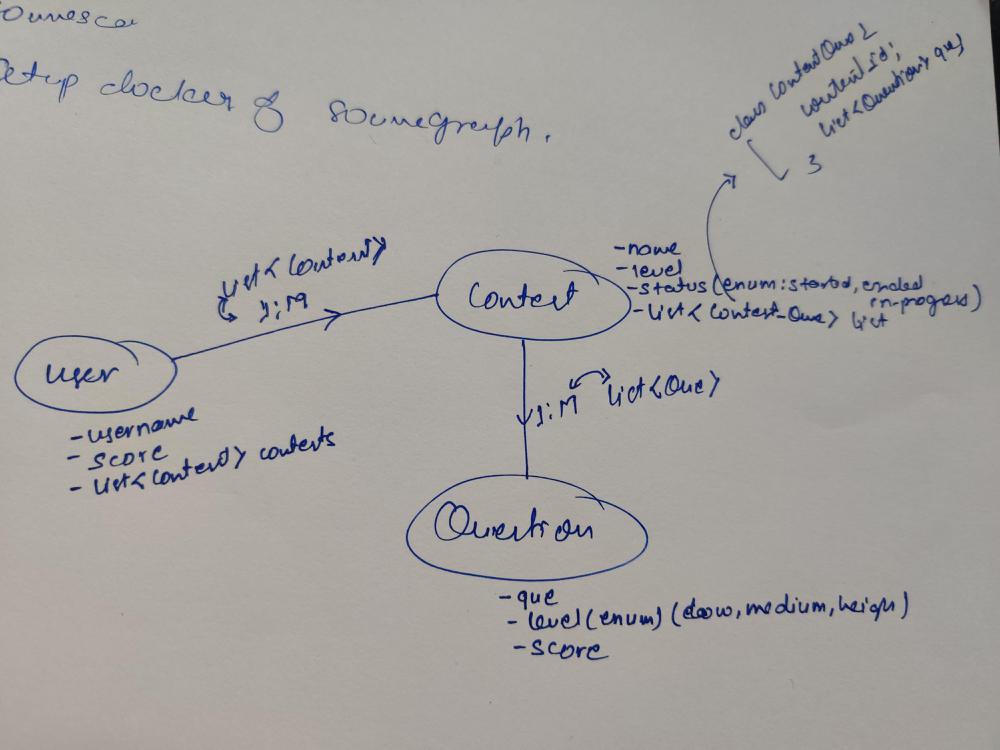
Now Add other fields of entities
User:
username
score
List<Contest> contests -- (A)
Contest:
name
level
status
List<Question> questions
Question:
question
level
score
Step 3: Store entities and write entities CRUD methods (Use Method 1)
Method 1: Use hashMap to store entities,
Map<Long, User> userDb
Map<Long, Question> questionDb
Map<Long, Contest> contestDb
Write CRUD method for each entity (HashMap sample example)
Method 2: Use H2 in memory using JPA, (simple to use but need to practice more)
Create 3 DAO class, internally with the help of the JPA class we can get all CRUD methods so no need to create any methods (JPA sample example)
Step 4: Create a service class for each entity and start implementing the requirement (service classes)
UserService:
createUser(username)
attendContest(contest id or contest object, username)
leaderBoard()
withdrawContest(contest id or contest object, username)
QuestionService:
createQuestion(question)
listAllQuestion()
ContestService:
createContest(contestId or contest object, username)
listAllContest()
runContest(contestid or contest object, username)
contestHistory()
add logic for above methods plus entity validation
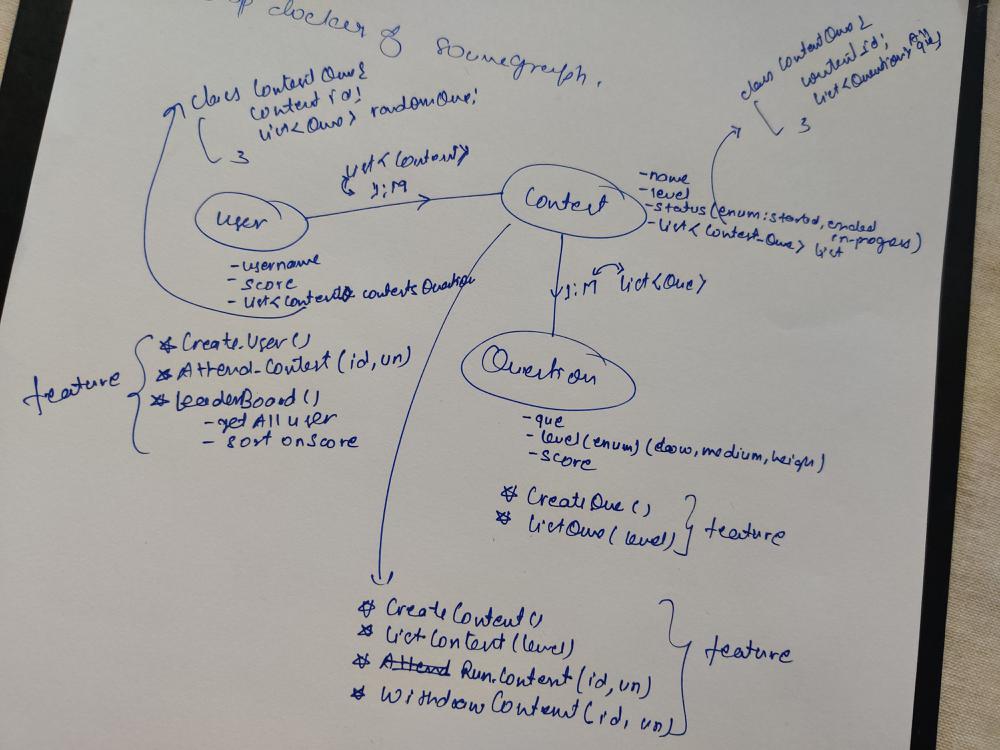
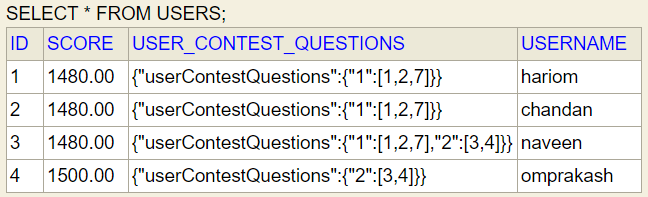
Step 5: Refactor code : extract class to an Interface, Abstract class, add enum, add exceptions, add constant, read from configList<Contest> contests --(A) become --> Map<Long, List<Long>> userContestQuestions = new HashMap<>(); KEY : Contest Id, Value: list of question ids
If we do Step-1 and Step-2 correctly then finally we can see entities tables (these tables are only visible in case of JPA but this entity relationships are also valid if we are using HashMap)
Contest entity
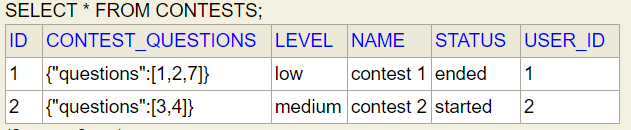
Question entity
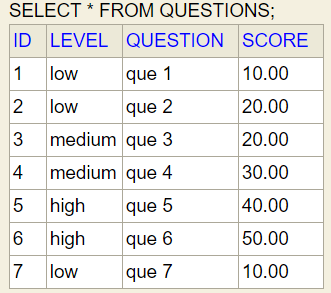
User entity
No comments:
Post a Comment